Imaging the He2
quantum halo state using a free electron laser
The helium
dimer (He2) is an intriguing quantum system. It is the most
loosely bound ground state molecule in the universe. It is an example for a
quantum halo state (a concept best known from nuclear physics), where 80% of
the density is in the classically forbidden region. By using the
COLTRIMS-technique we were able to image the wavefunction of this gigantic
diatomic molecule, detecting distances of up to 250 Angstrom – 500 times the
radius of the individual atoms.
The wavefunction shows a strictly exponential slope, a universal feature
across all energy scales in physics. The slope also gives a new value for
the long disputed helium dimer binding energy.
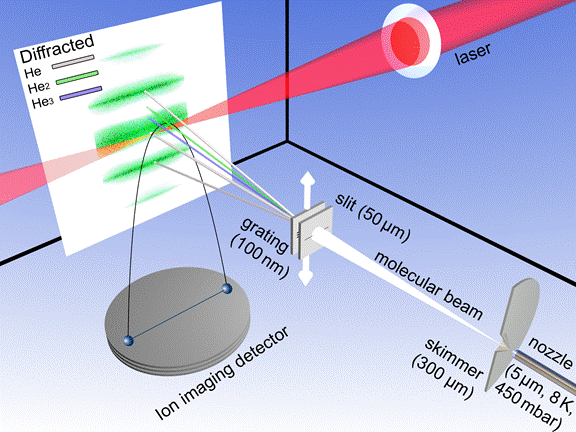
Figure 1:
How to image the He dimer (He2) wavefunction: A small amount of the
super fragile He dimers are produced in a cryogenically cooled nozzle expansion
(lower right). The gas beam, which contains about 1-2% dimers is send through a
transmission grating. By matter wave diffraction the helium atoms, dimers and
trimers are diffracted to different angles due to their different de Broglie
wavelength. An intense femtosecond laser or the light of the free electron laser
FLASH is focused onto the dimers in the beam. This leads to instantaneous
ionization of both atoms, the remaining singly charged ion coulomb explode and
are guided by an electric field onto a position sensitive detector in a COLTRIMS
reaction microscope.
We produced
helium clusters by expanding gaseous helium through a 5 μm nozzle, which
yields a range of different cluster sizes. To obtain a pure helium dimer target
beam we made use of matter wave diffraction. All clusters have the same velocity
but can be sorted by mass as their diffraction angle behind a transmission
grating (100 nm period) depends on their de Broglie wavelengths (λ =
h/mv, with Planck’s constant h, mass m and velocity v). That way only dimers
reach the laser focus while the dominant fraction of atomic helium as well as
the share of helium trimers present at the chosen gas expansion conditions get
deflected away from the ionization region. Figure 1 shows a schematic of the
setup.
The two atoms
constituting the dimer get singly ionized in the focus either via photoeffect
(free electron laser, FLASH, 18.5 nm) or via tunnelionization (Ti:Sa laser,
Dragon KMLabs, 780 nm). The two positively charged ions repel each other,
resulting in a Coulomb explosion. The Coulomb explosion converts the potential
energy of the two ions located at an internuclear distance R into a released
kinetic energy (KER) according to R = 1/KER.
By recording a
large number of Coulomb explosion events a distribution of measured distances R
is obtained (see Figure 2). This distribution represents a direct measurement of
the square of the helium dimer wavefunction |Ψ|². Theoretical calculations agree
well in the classically allowed part of |Ψ|² at the inner turning point. A
comparison of our measured probability density distribution close to the inner
turning point and some theoretical predictions are shown in Fig. 2B.
The classically
forbidden part of |Ψ|² is shown in Fig. 2C on a logarithmic scale. For
internuclear distances larger than 50 a.u. the helium dimer potential can be
approximated to zero. Accordingly, the wavefunction is approximated in this
region by the solution of the Schrödinger equation below a steplike barrier. The
solution is an exponentially decaying function, which is dependant on the height
of the potential step. Thus the binding energy can be extracted from the
measurement by an exponential fit to the pair-distance distribution, as depicted
in Fig. 2C. From the fit we obtain a helium dimer binding energy of 151.9 ± 13.3
neV.
Imaging the wave function of He2 granted an exclusive access to the tunneling region of a wavefunction below a potential step. We find the density of particles to decrease exponentially, confirming one of the few universal features of our world: the probability to find one of the constituents of bound matter far away is never zero but decreases exponentially – our experiment illustrates that general law
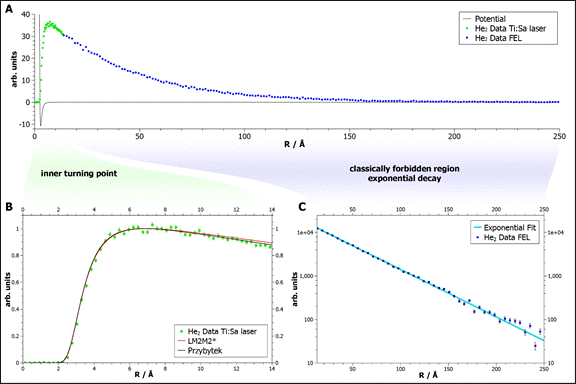
Figure 2: Measurement of the helium dimer wavefunction (A). Two detailed views show the important features of this quantum system: The region of the inner turning point (B) and the exponential decay in the classical forbidden region (C).
Publication:
Imaging the He2 quantum halo
state using a free electron laser
S. Zeller, M.
Kunitski, J. Voigtsberger, A. Kalinin, A. Schottelius, C. Schober, M. Waitz, H.
Sann, A. Hartung, T. Bauer, M. Pitzer, F. Trinter, C. Goihl, C. Janke, M.
Richter, G. Kastirke, M. Weller, A. Czasch,
M. Kitzler, M. Braune, R. E. Grisenti, W. Schöllkopf, L. Ph. H. Schmidt, M.
Schöffler, J. B. Williams, T. Jahnke, and R. Dörner
DOI:
10.1073/pnas.1610688113
PNAS (2016)
See online:
Press releases:
Goethe University Frankfurt (german press release)